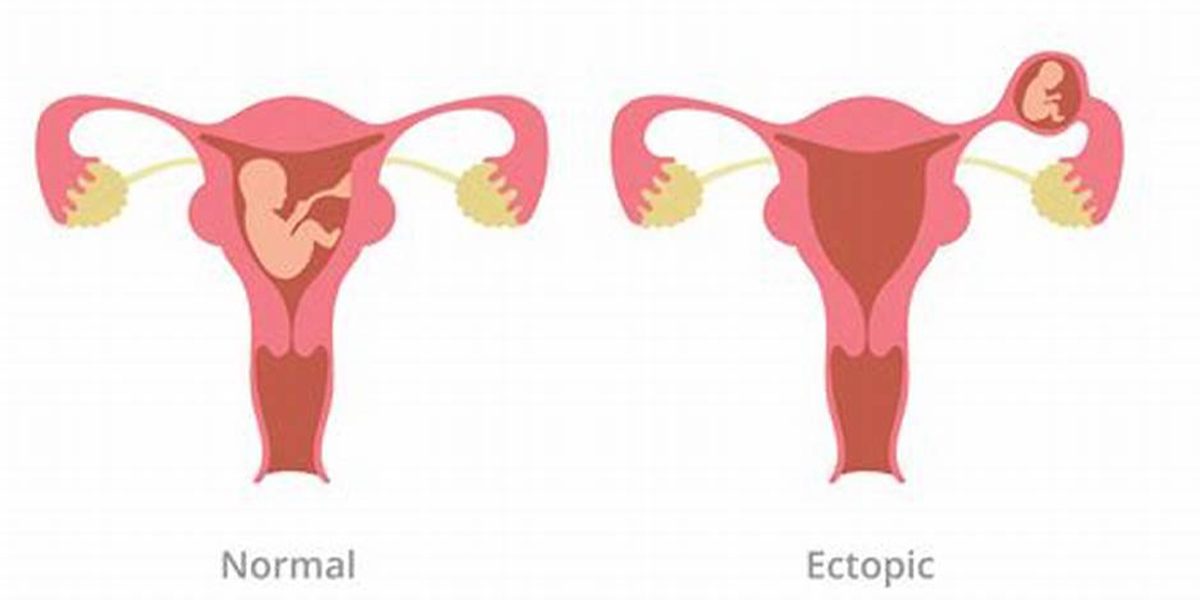
Ectopic Pregnancy – Its causes, symptoms and Treatment
In ectopic pregnancy, the foetus typically develops outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes (approximately 97.7% of cases). However, it can also implant in other locations such as the cervix, ovary, cornual region of the uterus, or abdominal cavity.
Main Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Moreover, conditions that slow down or block the movement of the egg down the fallopian tube may cause ectopic pregnancy.
Common reasons for ectopic pregnancy include:
- Presence of scar tissue.
- Swelling or inflammation resulting from previous pelvic surgery.
- Damage to the fallopian tubes.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
The main symptoms are:
- Vaginal bleeding distinct from regular menstrual bleeding.
- Lower abdominal pain, often on one side.
- Shoulder tip pain, occurring where the shoulder meets the arm.
- Discomfort experienced during bowel movements.
Further, the developing embryo cannot be saved in an ectopic pregnancy. Additionally, healthcare providers typically need to administer treatment to remove the pregnancy before it complicates further.
Treatments for Ectopic Pregnancy
The main treatment options are:
- Expectant management by careful monitoring to determine whether treatment is required.
- An Injection with methotrexate may be used to stop the growth of the pregnancy.
- Surgery to remove the embryo, typically along with the affected fallopian tube.
The doctor will recommend the remedy that is most suitable for you. Furthermore, the factors will mostly depend on your symptoms, the size of the fetus, and the level of pregnancy hormone (human chorionic gonadotropin, or hCG) in your blood.
1. Expectant management
Additionally, if the symptoms are mild and the pregnancy is very small or cannot be located, close monitoring may suffice. In many cases, there’s a good chance that the Ectopic pregnancy will resolve on its own without intervention. Also, we refer to this approach as expectant management.
The following is likely to happen:
- You’ll need to take regular blood tests to check that the level of hCG in your blood is decreasing.
- Further treatment may be necessary if your hormone level doesn’t decrease or if it increases.
- You’ll usually experience some vaginal bleeding.
- You may also have some abdominal pain.
- You’ll receive further guidance on what to do if you develop more severe symptoms.
2. Medications
Generally, healthcare providers may recommend a medication called methotrexate to terminate the ectopic pregnancy. However, doctors administer this composition to stop the pregnancy from growing.
Some side effects of methotrexate include:
- Stomach pain
- Dizziness
- Feeling sick
- Diarrhoea
3. Surgery
In many cases, surgeons will perform keyhole surgery (laparoscopy) to remove the pregnancy before it grows too large.
During a laparoscopy:
- During a laparoscopy, the medical team administers general anesthesia, so you’re asleep while they perform the procedure.
- Small cuts or incisions are made in your abdomen
- A laparoscope and small surgical instruments are inserted through the incisions
- The fallopian tube containing the pregnancy is removed
To Conclude
If there is any suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention from your healthcare provider. Prompt evaluation and treatment can help prevent or minimize potential harm to your body.
At Jeevan Fertility and Women Care Clinic, we prioritize the health and well-being of our patients and offer exceptional services. As a leading women’s care clinic in Chennai, we dedicate ourselves to providing the highest quality care and support to our patients.